Economy
How The Pandemic Could Force A Generation Of Mothers Out Of The Workforce
For the past few months, Alicia Wertz has barely seen her husband. Since schools closed in their northern Alabama town in March, they’ve been single-mindedly focused on a single goal: making sure that someone was watching their three kids. At first, Wertz tried working from home. But she wasn’t getting anything done, so they tried splitting the hours: Wertz’s husband watches the children in the morning, then a sitter comes to relieve him in the afternoon until Wertz takes over when she returns from work.
“When we’re not working, we’re by ourselves with the children. It almost feels like you’re a single parent. All you do is go to work and care for the kids,” Wertz said.
In her mind, Wertz is counting down the days until schools reopen. But there’s a nagging worry at the back of her head — what if they don’t open at all? “The thought of [my kids] not going back in the fall is devastating,” Wertz said when we spoke in early July. “It raises this question of — if one of us has to stay home with the children, whose job is more important? I think it was something that we did have conversations about before, but COVID-19 has made it much worse.”
[Related: Where The Latest COVID-19 Models Think We’re Headed — And Why They Disagree]
Wertz isn’t the only working mother for whom the thought of the fall calendar sparks both relief and dread. And what comes next could have disproportionate — and long-lasting — effects on the careers of countless women across the country. Studies have shown that women already shoulder much of the burden of caring for and educating their children at home; now, they’re also more likely than men to have lost their jobs thanks to the pandemic. And the collapse of the child care and public education infrastructure that so many parents rely on will only magnify these problems, even pushing some women out of the labor force entirely.
“We’re in danger of erasing the limited gains we’ve made for women over the past few decades, and especially women of color,” said Melissa Boteach, Vice President for Income Security and Child Care/Early Learning at the National Women’s Law Center.
The crux of the issue: Child care just isn’t as available as it was before the pandemic. Data provided to FiveThirtyEight by the job-search website Indeed shows that child-care services have been much slower to hire again (a useful proxy for re-opening) than other areas of the economy:
Combine that with the news that many schools will remain closed in the fall, and it’s easy to see the crisis at hand. If polling is any indication, the vast majority of the fallout is being weathered by mothers, who were already doing the majority of household work even before the pandemic began.
In 2015, the Pew Research Center asked parents about how they divide family responsibilities when both work full-time.1 Some tasks were split relatively evenly: Twenty percent of respondents said the mother disciplined children more, 17 percent said the father disciplined more, and 61 percent said that responsibility was shared equally. For every task, however, more respondents reported that the mother carried a greater amount of the load than those who said the father did — including areas involving managing children’s schedules, caring for children when they’re sick and handling household chores.
Moms usually shoulder more of the load at home
Share of parents in households with two full-time working parents who say each parent does more work in a given category, according to a Pew poll
| Share of parents who say… | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Mother does more | Father does more | Work split equally |
| Managing children’s schedules/activities | 54% | 6% | 39% |
| Taking care of sick children | 47 | 6 | 47 |
| Handling household chores, etc. | 31 | 9 | 59 |
| Playing/doing activities with children | 22 | 13 | 64 |
| Disciplining children | 20 | 17 | 61 |
Along similar lines, Pew also found in a poll from 2019 that 80 percent of women living with a partner who had children did the primary grocery shopping and meal-preparation duties for their families. And according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ American Time Use Survey — which tracks the average amount of time people spend per day on different categories of activity — married mothers with full-time jobs spent 56 percent more time doing childcare and housework than corresponding fathers. By contrast, fathers spent more time on work-related tasks, travel and leisure activities.2
All that extra time moms spend really adds up
Daily time spent doing various activities by married parents of children under 18 who both worked full-time, according to the American Time Use Survey
| Hours spent per day | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Activity | Mothers | Fathers | Diff. |
| Household activities | 1.87 | 1.23 | +0.64 |
| Physical care for children | 0.59 | 0.28 | 0.31 |
| Child care - other | 0.36 | 0.22 | 0.14 |
| Child-related travel | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| Education-related activities | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| Reading with children | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Playing/hobbies with children | 0.27 | 0.29 | -0.02 |
| Total | 3.49 | 2.24 | 1.25 |
Even under normal circumstances, it was difficult for mothers of young children to balance work against the heavy burden of child care. The BLS found that in 2019, the labor force participation rate for women with children under age 6 was 66.4 percent, well below the rate for women with children age 6 or older3 (76.8 percent). According to a 2014 survey by the U.S. Census Bureau, 61 percent of women who were out of a job and have young children listed “caretaking” as a reason why they were not employed. Forty-six percent of women who were out of a job and have older children said the same. To put that in perspective, only 10 percent of all respondents who were out of work gave caregiving as a reason.4
A similar strain is apparent in working mothers’ decisions to take unpaid leave, or even part-time jobs instead of full-time ones. According to that same census survey from 2014, 30 percent of women who were part-time workers with young children — and 19 percent of women with older children — said caretaking was a reason they worked part-time. (Among part-time workers, the overall share is just 7 percent.)5
Now, with schools closed and day cares struggling to remain open, even more women may conclude that the best — or perhaps the only — choice for their family and their own sanity is to reduce their hours, or even press “pause” on their career.
“Sometimes I’ll get to a point where I’m like, ‘I’m so tired, I’ll have to go part-time to make it all work,’” said Lee Dunham, a lawyer who lives in Delaware. Since the pandemic started, Dunham has been mostly responsible for her 10-month-old daughter during the day — which means her work day doesn’t start until 8 p.m. and usually wraps around 2 a.m.. “I’m just basically not getting enough sleep because I’m watching the baby 40 hours a week and doing my job 40 hours a week. It’s really rough.”
Dunham feels she’s lucky to have an understanding employer who told her earlier this year that they’d be cutting all of their employees some slack because of the pandemic. But at the time, she added, everyone was assuming day care would be up and running by mid-summer. “It might be that I have to dial back my hours, which of course means I will get paid less.”
Subscribe to our coronavirus podcast, PODCAST-19
This kind of calculus already depresses women’s wages and makes it harder for their careers to progress. According to the National Women’s Law Center, mothers are typically only paid 71 cents for every dollar paid to fathers. In fact, a lot of recent research into the gender pay gap has found that much of it is simply due to the constraints on working mothers. For instance, a 2018 analysis of data from Denmark — which offers a counterpoint to the United States in terms of social safety net, yet still has a very large and persistent gender wage gap — found that women’s earnings drop significantly after having their first child, while men’s earnings aren’t affected at all. And crucially, several studies in the U.S. and other countries have found that the trajectory of wages for women who don’t have children resembles those of men, whether they have kids or not (although some research has actually suggested that becoming a father can contribute to men’s career success).
This disparity is particularly intense for women of color. Black mothers are paid only 54 cents for every dollar paid to a white father, according to NWLC; for Latina mothers, it’s 46 cents. Low-income women of color are also among the likeliest to have lost their jobs in the current recession. And they’re disproportionately likely to be the child-care workers who are being asked to come back to work, sometimes in unsafe working conditions, for low wages. “We’re in a vicious cycle where we need child care as one of the tools to get women to equal pay, and yet unequal pay is one of the primary reasons that women are pushed into staying home,” Boteach said.
[Related: How Americans View The Coronavirus Crisis And Trump’s Response]
Leaving the workforce, even if it’s just for a year or two, has ripple effects that can follow a woman for the rest of her life, even depressing her earnings in retirement. Finding a new job after a few years on hiatus can be very difficult for mothers, who may be stereotyped as less serious about their careers because they took time off to be with their children. One study from 2007 found that mothers were perceived to be less competent than fathers, and their recommended salaries were also lower.
During this pandemic, you can already see the disproportionate impact taking shape. The unemployment rate for women in April was 16.2 percent, higher than it has been in any month since at least 1948, before dropping to 11.7 percent in June — a percentage point higher than the rate for men (10.6 percent). Even more striking, labor force participation for women dipped to 54.7 percent in April before rising to 56.1 percent last month. Both of those numbers are reminiscent of the rates for women from the 1980s — back when the very notion of women in the workforce was still gaining momentum.6
Wertz has no plans to leave her job — at least for now. “I worked incredibly hard to get to where I am now,” she said. “I essentially paid my way through school with no family support. For years I worked entirely too hard for not enough money.” Already, she worries that she’s perceived differently in the workplace because she’s a mother. “Even if it was just a year, I know how that gap would look on my resume,” she said. “If I had to take that step back, I just don’t know if I’d recover from it.”
Economy
Afranius & Petreius Fear Caesar’s Cavalry & Decide to Retreat: Liveblogging the Fall of the Roman Republic
Caesar faces Pompeian forces split in two: an army without a leader in Spain, and a leader without an army in Greece. Logistics and diplomacy reverse the situation at Ilerda in northeast Spain, as Caesar gains an advantage in allied cavalry that makes Afranius and Petreius fear their position will soon become logistically untenable. They decide to retreat:
Gaius Julius Caesar: The Civil War http://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/10657/pg10657-images.html: ‘When news of this battle was brought to Caesar at Ilerda, the bridge being completed at the same time, fortune soon took a turn. The enemy, daunted by the courage of our horse, did not scour the country as freely or as boldly as before: but sometimes advancing a small distance from the camp, that they might have a ready retreat, they foraged within narrower bounds…
…at other times, they took a longer circuit to avoid our outposts and parties of horse; or having sustained some loss, or descried our horse at a distance, they fled in the midst of their expedition, leaving their baggage behind them; at length they resolved to leave off foraging for several days, and, contrary to the practice of all nations, to go out at night.
In the meantime the Oscenses and the Calagurritani, who were under the government of the Oscenses, send ambassadors to Caesar, and offer to submit to his orders. They are followed by the Tarraconenses, Jacetani, and Ausetani, and in a few days more by the Illurgavonenses, who dwell near the river Ebro. He requires of them all to assist him with corn, to which they agreed, and having collected all the cattle in the country, they convey them into his camp. One entire cohort of the Illurgavonenses, knowing the design of their state, came over to Caesar, from the place where they were stationed, and carried their colours with them.
A great change is shortly made in the face of affairs. The bridge being finished, five powerful states being joined to Caesar, a way opened for the receiving of corn, and the rumours of the assistance of legions which were said to be on their march, with Pompey at their head, through Mauritania, having died away, several of the more distant states revolt from Afranius, and enter into league with Caesar.
Whilst the spirits of the enemy were dismayed at these things, Caesar, that he might not be always obliged to send his horse a long circuit round by the bridge, having found a convenient place, began to sink several drains, thirty feet deep, by which he might draw off a part of the river Segre, and make a ford over it. When these were almost finished, Afranius and Petreius began to be greatly alarmed, lest they should be altogether cut off from corn and forage, because Caesar was very strong in cavalry.
They therefore resolved to quit their posts, and to transfer the war to Celtiberia.
There was, moreover, a circumstance that confirmed them in this resolution: for of the two adverse parties, that which had stood by Sertorius in the late war, being conquered by Pompey, still trembled at his name and sway, though absent: the other which had remained firm in Pompey’s interest, loved him for the favours which they had received: but Caesar’s name was not known to the barbarians. From these they expected considerable aid, both of horse and foot, and hoped to protract the war till winter, in a friendly country.
Having come to this resolution, they gave orders to collect all the ships in the river Ebro, and to bring them to Octogesa, a town situated on the river Ebro, about twenty miles distant from their camp. At this part of the river, they ordered a bridge to be made of boats fastened together, and transported two legions over the river Segre, and fortified their camp with a rampart, twelve feet high…
.#history #livebloggingthefalloftheromanrepublic #politics #2020-08-11
html < >
edit html < >
Foreshadowing from Gaius Sallustius Crispus https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/foreshadowing-from-gaius-sallustius-crispus-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: A strongly unconventional high politician facing the expiration of his term of office. He knows that there is a very high probability that, because of his actions in office, his adversaries will try and convict him of crimes after he lays down his power. Let us start with some foreshadowing from Gaius Sallustius Crispus…
Pompey’s Strategy and Domitius’ Stand https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/burns-pompeys-strategy-and-domitius-standnoted.html: In his The Civil War Gaius Julius Caesar presented “just the facts” in a way that made Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus look like a cowardly and incompetent idiot. The attractive interpretation is that Ahenobarbus was just trying to do the job of defeating Caesar, but had failed to recognize that Pompey was not his ally. Pompey, rather, was somebody whose first goal was to gain the submission of Ahenobarbus and the other Optimates, and only after that submission was gained would he even think about fighting Caesar. Still an idiot, but not an incompetent or a cowardly one: Alfred Burns https://github.com/braddelong/public-files/blob/master/readings/article-burns-pompey.pdf: ‘In early 49, the alliance confronting Caesar consisted of the old republican senate families who under the leadership of [Lucius] Domitius [Ahenonbarbus] tried to maintain the traditional institutions and of Pompey who clung to his own extra-legal position of semi-dictatorial power. Both parties to the alliance were as mutually distrustful as they were dependent on each other…
Marcus Tullius Cicero’s Take on the First Three Months of -49 https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/marcus-tullius-ciceros-take-on-the-first-three-months-of-49-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: ‘We have a primary source for the start of the Roman Civil Warin addition to Gaius Julius Caesar’s deceptively powerful plain-spoken “just the facts” narrative in his Commentaries on the Civl War—a narrative that is also a clever and sophisticated lawyer’s brief. Our one other primary source: Marcus Tullius Cicero’s letters to his BFF Titus Pomponius Atticus. Caesar, in his The Civil War, makes himself out to be reasonable, rational, decisive, and clever. Cicero, in his Letters to Atticus is a contrast. He lets his hair down. He is writing to someone he trusts to love him without reservation. He is completely unconcerned with making himself appear to be less flawed than he appears. And the impression he leaves is absolutely dreadful: he makes himself out to be erratic, emotional, dithering, and idiotic…
Reflecting on the First Three Months of -49 https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/reflecting-on-the-first-three-months-of-49-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: ‘The key question for the first three months of the year -49 is: what did the factions anticipate would happen in that year? The Optimates seemed to think that they had Caesar cornered: Either he surrendered… and then submitted to trial… or he… was quickly crushed…. Cicero appears to have believed that either the Senate surrendered to Ceesar and let him… put Cataline’s conspiracy into action but legally… and then ruled With the support of his electoral coalition of mountebank ex-debtors and ex-veterans to whom he had given land; or… Pompey… crushed Cesar militarily… follow[ed] up with proscriptions and executions after which he would rule as a second Sulla. What is not at all clear to me is what Pompey thought would happen…. My guess, reading between the lines of Plutarch, is that Pompey found himself allied with the Senate in January-February of -49, but not in command of anything—as shown by Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus’s behavior at Corfinium, attempting to trap Pompey into fighting alongside him in central Italy. And so he retreated to Greece, where he was in undisputed command…
Caesar Offers a Compromise Solution (or So Caesar Says) https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/caesar-offers-a-compromise-solution-or-so-caesar-says-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: The Beginning of Caesar’s Commentaries on the Civil War, in which Caesar says that he had proposed a compromise solution to the political crisis…. ‘The dispatch from Gaius Caesar was delivered to the consuls; but it was only after strong representations from the tribunes that they gave their grudging permission for it to be read in the Senate. Even then, they would not consent to a debate on its contents, but initiated instead a general debate on ‘matters of State’…. Scipio spoke… Pompey, he said, intended to stand by his duty to the State, if the Senate would support him; but if they hesitated and showed weakness, then, should they want his help later, they would ask for it in vain…
The Optimate Faction Rejects Caesar’s Compromise https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/the-optimate-faction-rejects-caesars-compromise-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: Caesar narrates the reasons that the leaders of the Optimate faction—Cato, Lentulus, Scipio, and Pompey—worked hard to set the stage for war, and how the majority of Senators in the timorous middle were robbed of the power to decide freely, and driven reluctantly to vote for Scipio’s motion to rob Caesar of his protections against arrest and trial…
The Optimate Faction Arms for War, & Illegally Usurps Provincial Imperium https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/the-optimate-faction-arms-for-war-illegally-usurps-provincial-imperium-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: Caesar narrates: Whatever norms he may or may not have broken during his consulate—in order to wrest land from the hands of corrupt plutocrats and grant it to the deserving—he says, the Optimate faction does much worse. In the first seven days of the year of the consulate of Lucius Cornelius Lentulus Crus and Gaius Claudius Marcellus Maior, the Optimate faction goes beyond norm-breaking into outright illegality. And to that they add impiety. They illegaly seize power, as they grant themselves proconsular and propraetorial imperium over the provinces, without the constitutionally-required popular confirmation of imperium. They impiously violate the separation of church and state by seizing temple funds for their own use. They thus incur the wrath of the gods. And they incur the enmity of all who believe in constitutional balance, as opposed to armed plutocratic dictatorship…
Caesar Presents His Case to the 13th Legion, & Negotiates Unsucccessfully with Pompey https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/caesar-presents-his-case-to-the-13th-legion-negotiates-unsucccessfully-with-pompey-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-rep.html: Caesar presents his case to the 13th Legion, and wins its enthusiastic support. Caesar and Pompey negotiate, but Pompey refuses to give up his dominant position. He holds imperium over Spain and commanding the ten Spanish garrison legions, while also residing in the suburbs of Rome and thus dominating the discussions of the Senate. Pompey refuses to commit to setting a date for his departure for Spain…
The Optimate Faction Panics and Abandons Rome https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/the-optimate-faction-panics-and-abandons-rome-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: Caesar narrates: The Optimate faction panics at a rumor of Caesar’s approach, and flees from Rome with the looted Treasury reserve. The towns of Italy support Caesar. Even the town of Cingulum rallied to Caesar, even though its founder Titus Labienus, Caesar’s second-in-command in the Gallic War, had deserted Caesar for his earlier allegiance to Pompey. And Pompey’s attempts to reinforce his army by recruiting veterans who had obtained their farms through Caesar’s legislative initiatives did not go well…
Caesar Besieges Domitius in Corfinum https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/caesar-besieges-domitius-in-corfinum-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus began raising troops, and by the start of February -49 had 13000 soldiers in the town of Corfinum. On 09 Feb -49 Domitius decided to stand at Corfinum rather than retreat to the south of Italy. So he wrote to Pompey… urged that the Optimate faction join its military forces together at Corfinum to outnumber and fight Caesar. Pompey disagreed. Why did he decide that he, Pompey, “cannot risk the whole war in a single battle, especially under the circumstances”?…
Caesar Captures Corfinum https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/caesar-captures-corfinum-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus’s deception that Pompey is coming to the Optimates’ aid in Corfinum falls apart, Ahenobarbus tries to flee, Lentulus Spinther begs for his life, Caesar grants clemency to all, and adds the three Optimate and Pompeian legions to his army. Before Corfinum Caesar had had two legions in Italy to the Optimate and Pompeian six. After Corfinum (with the arrival of Legio VIII plus new recruits) Caesar has seven legions in Italy to the Pompeian three. It is now 21 Feb -49: Gaius Julius Caesar: The Civil War: ‘Domitius’s looks, however, belied his words; indeed, his whole demeanour was much more anxious and fearful than usual. When to this was added the fact that, contrary to his usual custom, he spent a lot of time talking to his friends in private, making plans, while avoiding a meeting of the officers or an assembly of the troops, then the truth could not be concealed or misrepresented for long…
Pompey Refuses to Negotiate & Flees to Greece https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/pompey-refuses-to-negotiate-flees-to-greece-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: Pompey flees to the southern Adriatic port of Brundisium. Caesar catches up to him and begs him to negotiate. Pompey refuses and flees to Greece. Caesar decides not to follow, but to turn and first defeat the Pompeian armies in Spain. It is now 18 Mar -49…
Cementing Caesarian Control of the Center of the Empire: Late March -49 https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/cementing-caesarian-control-of-the-center-of-the-empire-late-march-49-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: Caesar, now that the Pompeians and the High Optimates have fled, offers to share power with the dysfunctional Senate but, filibustered and vetoed by Optimate tribunes, he consolidates his hold on the center of the empire and heads for Spain…
Treachery at Massilia: April-May -49 https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/07/treachery-at-massilia-april-may-49-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: The Massiliotes profess neutrality—until Pompeian reinforcements arrive, and then they go back on their word. Pompeians to whom Caesar had shown clemency at Corfinium have again taken up weapons against him: Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus at Massilia, and Vibullius Rufus to command the Pompeian legions in Spain…
Rendezvous in Spain, at Ilerda https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/08/rendezvous-in-spain-at-ilerda-livelogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-repubvlic.html: Caesar’s first probing military moves demonstrate his position is very strong. From a central position in control of the heart of the empire, he moves first to deal with the Pompeian forces in Spain to his west: ‘The First Spanish Campaign: Fabius’s orders were to make haste to seize the passes over the Pyrenees, which at that time were being held by the troops of Pompey’s lieutenant, Lucius Afranius. He ordered the remaining legions, which were wintering farther away, to follow on. Fabius, obeying orders, lost no time in dislodging the guards from the pass and proceeded by forced marches to encounter Afranius’s army…
Caesar Begins His First Spanish Campaign https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/08/caesar-begins-his-first-spanish-campaign-livelogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: A strongly unconventional high politician knows that his adversaries will try and convict him of crimes after he lays down his military command, so he lets the dice fly. His first probing military moves demonstrate his position is very strong. He moves first to deal with the Pompeian forces in Spain to his west. He has his men build a fortified camp close enough to the Pompeian base that the soldiers will inevitably start to fraternize…
Heavy But Inconclusive Skirmishing Between the Military Camps at Ilerda https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/08/heavy-but-inconclusive-skirmishing-between-the-military-camps-at-ilerda-livelogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: ‘From a central position in control of the heart of the empire, Caesar moves first to deal with the Pompeian forces in Spain to his west. Heavy but inconclusive skirmishing follows…
Floods and Supply Lines: Livelogging the Fall of the Roman Republic https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/08/floods-and-suppyl-liner-livelogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: From a central position in control of the heart of the empire, Caesar moves first to deal with the Pompeian forces in Spain to his west: Gaius Julius Caesar: The Civil War: ‘Floods and Supply Lines: The enemy fortified the hill, about which the contest had been, with strong works, and posted a garrison on it. In two days after this transaction, there happened an unexpected misfortune. For so great a storm arose, that it was agreed that there were never seen higher floods in those countries; it swept down the snow from all the mountains, and broke over the banks of the river, and in one day carried away both the bridges which Fabius had built, a circumstance which caused great difficulties…
Caesar Turns the Tables on the Pompeian Skirmishers https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/08/caesar-turns-the-tables-on-the-pompeian-skirmishers-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: ‘Caesar faces Pompeian forces split in two: an army without a leader in Spain, and a leader without an army in Greece. With clever engineering and tactics, he overcomes his logistical difficulties and begins to turn the tables on the Pompeian army in Spain…
The Caesarian Navy Led by Decimus Brutus Wins a Victory at Massilia https://www.bradford-delong.com/2020/08/the-caesarian-navy-led-by-decimus-brutus-wins-a-victory-at-massilia-liveblogging-the-fall-of-the-roman-republic.html: ‘Caesar faces Pompeian forces split in two: an army without a leader in Spain, and a leader without an army in Greece. While Caesar grapples with the leaderless Pompeian army in Spain, Decimus Brutus and Caesar’s navy win an victory over the traitorous Massilians and Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus…
Economy
Dorothy Theresa Sawchak Mankiw
Above is a picture of my mother as a young woman. I would like to tell you about her.
My mother was born on July 18, 2020, the second child of Nicholas and Catherine Sawchak.
Nicholas and Catherine were immigrants from Ukraine. They came to the United States as teenagers, arriving separately, neither with more than a fourth-grade education. Catherine was from a farming area in western Ukraine. She left because her family wanted her to marry an older man rather than her younger boyfriend, who had been conscripted into the army. Her first job here was as a maid. Nicholas was from Kiev, where he had been trained to be a furrier. In the United States, he worked as a potter, making sinks and toilettes. When Nicholas and Catherine came to the United States, they thought they might return home to Ukraine eventually. But World War I and the Russian Revolution intervened, causing a change of plans. Catherine’s boyfriend died in the war. Nicholas and Catherine met each other, married, and settled in a small row house in Trenton, New Jersey, where they lived the rest of their lives.
Catherine and Nicholas had two children, my uncle Walter and my mother Dorothy. When my mother was born, her parents chose to name her “Dorothy Theresa Sawchak.” But because Catherine spoke with a heavy accent, the clerk preparing the birth certificate did not understand her. So officially, my mother’s middle name was “Tessie” rather than “Theresa.” She never bothered to change it.
Nicholas and Catherine were hardworking and frugal. They saved enough to send Walter to college and medical school. He served as a physician in the army during the Korean war. Once I asked him if he worked at a MASH unit, like in the TV show. He said no, he worked closer to the front. He patched up the wounded soldiers the best he could and then sent them to a MASH unit to recover and receive more treatment. After the war, he became a pathologist in a Trenton-area hospital. He married and had two daughters, my cousins.
My mother attended Trenton High School (the same high school, I learned years later, attended by the economist Robert Solow at about the same time). She danced ballet. She water-skied on the Delaware River. She loved to read and go to the movies.
In part because of limited resources and in part because of the gender bias of the time, my mother was not given the chance to go to college. Years later, her parents would say that not giving her that opportunity was one of their great regrets. Instead, my mother learned to be a hairdresser. She was also pressured to marry the son of some family friends.
The marriage did not work. With my mother pregnant, her new husband started “running around,” my mother’s euphemism for infidelity. They divorced, and she kicked him out of her life. But the marriage did leave her with one blessing—my sister Peg.
My mother continued life as a single mother. Some years later, she met my father, also named Nicholas, through social functions run by local Ukrainian churches. They both loved to dance. He wanted to marry her, but having been burned once, she was reluctant at first. Only when she realized that he had become her best friend did she finally accept.
In 1958, nine months after I was born, Mom, Dad, Peg, and I left Trenton for a newly built split-level house in Cranford, New Jersey. My father was working for Western Electric, an arm of AT&T, first as a draftsman and then as an electrical engineer. He worked there until his retirement. One of his specialties was battery design. When I was growing up, I thought it sounded incredibly boring. Now I realize how important it is.
My mother then stopped working as a hairdresser to become a full-time mom. But she kept all the hairdresser equipment from her shop—chair, mirrors, scissors, razors, and so on—in our basement. She would cut the hair of her friends on a part-time basis. When I was a small boy, she cut my hair as well.
I attended the Brookside School, the public grade school which was a short walk from our house. When I was in the second or third grade, my mother was called in to see the teacher. The class had been given some standardized aptitude test. “Greg did well,” the teacher said. “We were very surprised.”
At that moment, my mother decided the school was not working out for me. I was talkative and inquisitive at home but shy and lackluster at school. I needed a change.
She started looking around for the best school she could find for me. She decided it was The Pingry School, an independent day school about a dozen miles from our house. She had me apply, and I was accepted.
The question then became, how to pay for it? Pingry was expensive, and we did not have a lot of extra money. My mother decided that she needed to return to work.
She started looking for a job, and an extraordinary opportunity presented itself. Union County, where we lived, was opening a public vocational school, and they were looking for teachers. She applied to be the cosmetology teacher and was hired.
There was, however, a glitch. The teachers, even though teaching trades like hairdressing, needed teacher certification. That required a certain number of college courses, and my mother had not taken any. So she got a temporary reprieve from the requirement. While teaching at the vocational school during the day, she started taking college courses at night to earn her certification, all while raising two children.
My mother taught at the vocational school until her retirement. During that time, she also co-authored a couple of books, called Beauty Culture I and II, which were teacher’s guides. From the summary of the first volume: “The syllabus is divided into six sections and includes the following areas of instruction: shop, school, and the cosmetologist; sterilization practices in the beauty salon; scalp and hair applications and shampooing; hair styling; manicuring; and hairpressing and iron curling.” I suppose one might view this project as a harbinger of my career as a textbook author.
When my parents both retired, they were still the best of friends. They traveled together, exploring the world in ways that were impossible when they were younger and poorer. During my third year as an economics professor, I was visiting the LSE for about a month. I encouraged my parents to come over to London for a week or so. They had a grand time. I believe it was the first time they had ever visited Europe. When I was growing up, vacations were usually at the Jersey shore.
My father died a few years later. My mother spent the next three decades living alone. She was then living full-time at the Jersey shore in Brant Beach on Long Beach Island. The house was close to the ocean and large enough to encourage her growing family to come for extended visits. Two children, five grandchildren, four great-grandchildren. The more, the merrier. Nothing made her happier than being surrounded by family.
My mother loved to cook, especially the Ukrainian dishes she learned in her childhood. Holubtsi (stuffed cabbage) was a specialty. Another was kapusta (cabbage) soup. One time, the local newspaper offered to publish her kapusta soup recipe. They did so, but with an error. Every seasoning that was supposed to be measured in teaspoons was printed as tablespoons. The paper later ran a correction but probably to no avail. I am not sure if anyone ever tried the misprinted recipe and, if so, to what end.
During her free time in her later years, my mother read extensively, played FreeCell on her computer, and watched TV. A few years ago, when she was about 90 years old, I was visiting her, and I happened to mention the show “Breaking Bad.” She had not heard of it. She suggested we watch the first episode. And then another. And another. After I left, she binge-watched all five seasons.
As she aged, living alone became harder. When she had trouble going up and down the stairs, an elevator was added to her house. But slowly her balance faltered, and she fell several times. She started having small strokes, and then a more significant one. She moved into a nursing home. Whenever I visited, I brought her new books to read. Her love of reading never diminished.
This is, I am afraid, where the story ends. Last week, Dorothy Theresa Sawchak Mankiw tested positive for Covid-19. Yesterday, she died. I will miss her.
Source link
Economy
The GDP Collapse: It Is What It Is
Jim discussed elements of the 2020Q2 advance release on Thursday. Here, I amplify some aspects that he mentioned.
Confirmation: A Catastrophe in the Making
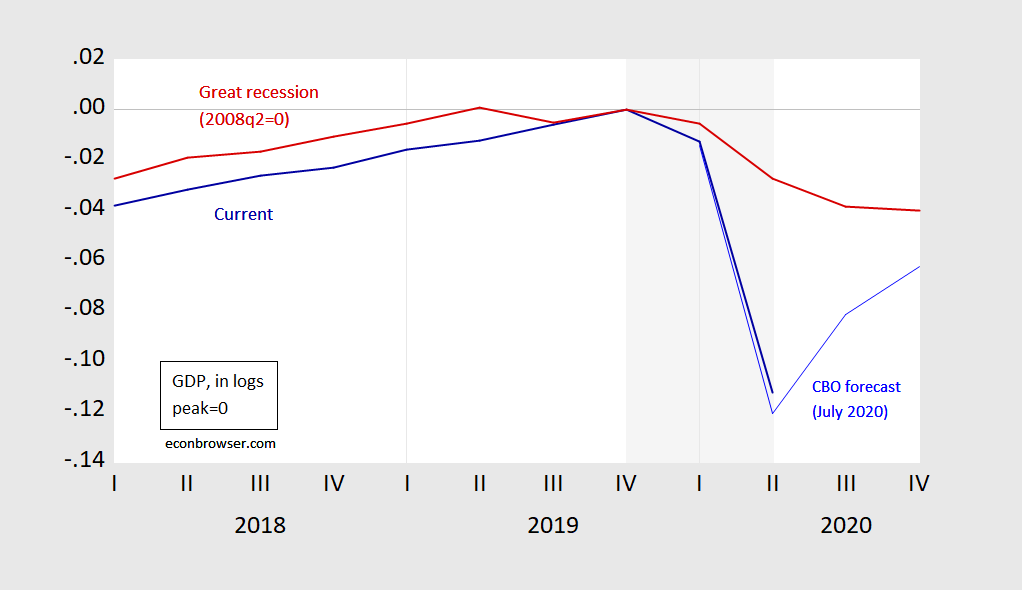
First, the Trump recession is truly catastrophic in scale; the pace of GDP decline is much greater than that in 2008. This is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: GDP in logs, normalized to 0 at 2019Q4 (NBER peak) (blue), and GDP normalized to 2008Q2 (red). NBER defined recession shaded gray, assuming trough at 2020Q2. Source: BEA, 2020Q2 advance release, CBO An Update to the Economic Outlook (July), NBER, author’s calculations.
A “No Confidence” Vote in Administration Policy and Investment
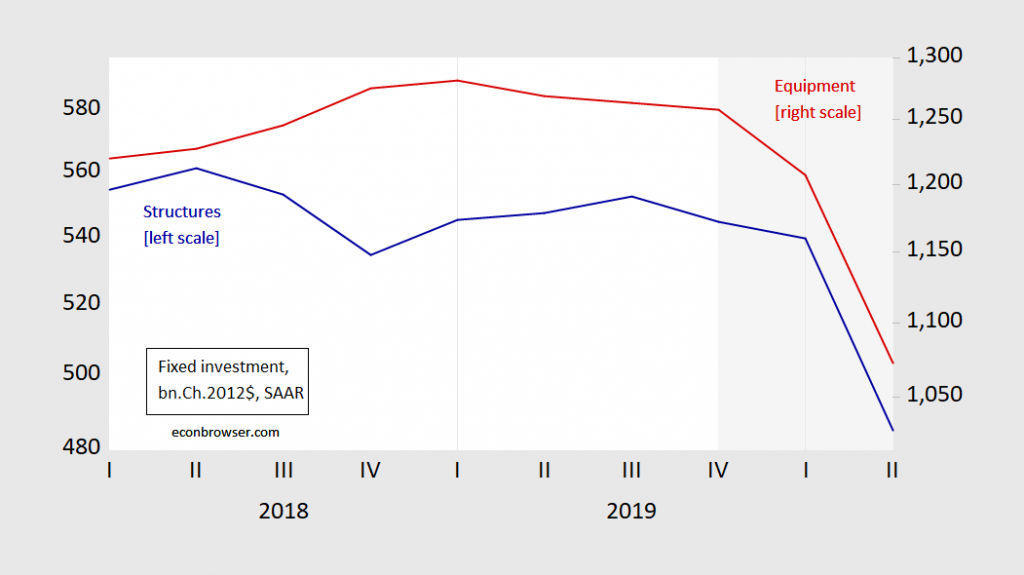
Second, investment has crashed — for both structures and equipment investment. That’significant insofar as capital investment is forward looking.
Figure 2: Fixed investment in structures (blue, left log scale), and in equipment (red, right log scale), in billions Chained 2012$, SAAR. NBER defined recession shaded gray, assuming trough at 2020Q2. Source: BEA, 2020Q2 advance release, NBER, author’s calculations.
This decline is even more rapid than in 2008Q4; 31.5% now vs. 24% then.
Figure 3: Nonresidential fixed investment in logs, normalized to 0 in 2019Q4 (blue), and normalized to 0 in 2008Q2 (red). NBER defined recession shaded gray, assuming trough at 2020Q2. Source: BEA, 2020Q2 advance release, NBER, author’s calculations.
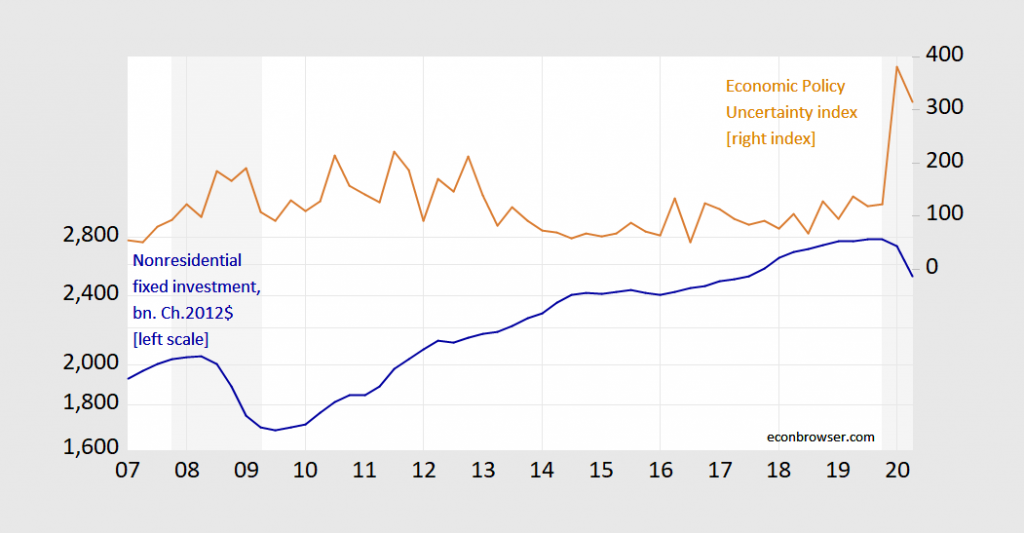
Certainly, some of the crash is due to the crash in aggregate demand — as in the 2007 recession — but some is due to uncertainty, including policy uncertainty. Policy uncertainty levels currently dwarf those of the Great Recession.
Figure 4: Nonresidential fixed investment in billions Chained 2012$ SAAR (blue, left log scale), Economic Policy Uncertainty index (tan, right scale). NBER defined recession shaded gray, assuming trough at 2020Q2. Source: BEA, 2020Q2 advance release, NBER, policyuncertainty.com via FRED, and author’s calculations.
No Recovery Without Recovery in Services Demand
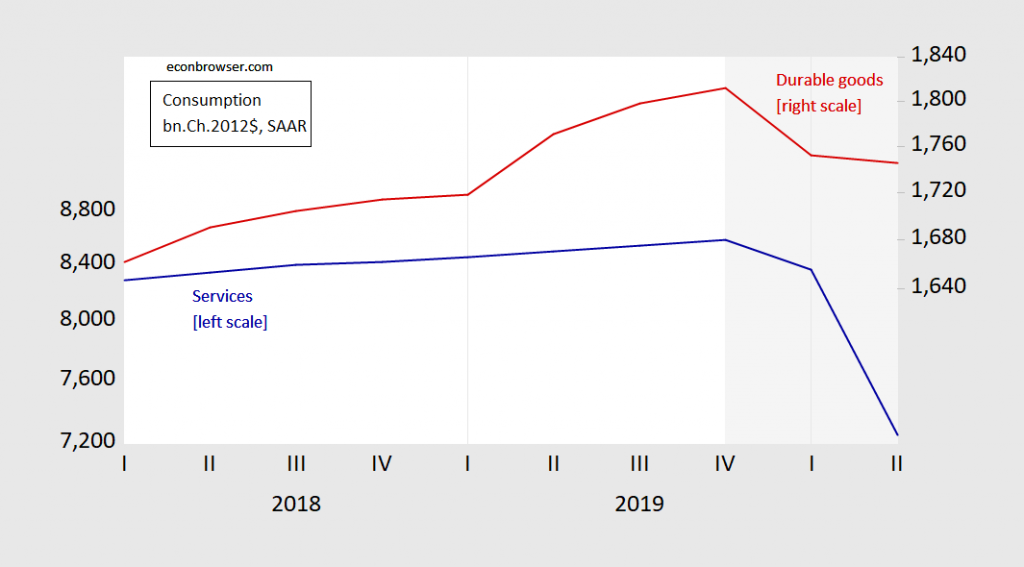
Third, this is a different kind of recession, in many ways, but importantly in the sectoral origin. As Jim Hamilton noted, the decline in services consumption was 43.5% on an annualized basis, while durable goods consumption was relatively flat.
Figure 5: Services consumption (blue, left log scale), and durable goods consumption (red, right log scale), all in billions Chained 2012$ SAAR. NBER defined recession shaded gray, assuming trough at 2020Q2. Source: BEA, 2020Q2 advance release, NBER, and author’s calculations.
Of the 9.8 percentage point decline in GDP (not annualized), 5.9 percentage points were accounted for (in a mechanical sense) by services consumption decline. Jim provides a breakdown of the services consumption decline in his post.
Services consumption will not fully recover until such time as the Covid-19 infection rates are at manageable levels that do not deter such consumption activities. The Administration’s current policy stance is unlikely to encourage that development; one could argue that it — in toto — is impeding that outcome.
State and Local Government Spending Collapses
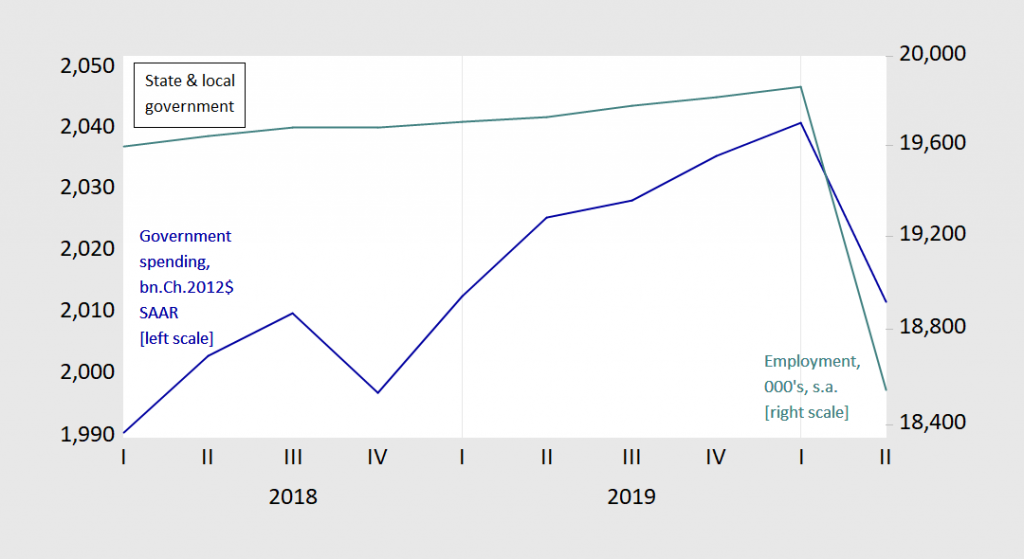
Fourth, the biggest threat to the economy may be avoidable. One of the lessons of the Great Recession is that constraints on state and local government spending — exacerbated by ill-advised state income tax cuts — was one of the reasons for the torpid pace of recovery. So far, we have not replicated completely that experience, but with Republican opposition to further Federal transfers to the state, we are in danger of repeating that error.
Figure 6: State and local government spending, billions Chained 2012$ SAAR (blue, left log scale), and state and local employment, 000’s, s.a. (teal, right log scale). Source: BEA 2020Q2 advance release, BLS employment situation June release.
This is why it is critical, as many economists have argued, for the next recovery package to include substantial aid to the states and localities.
-
 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks agoBernice King, Ava DuVernay reflect on the legacy of John Lewis
-
World News3 weeks ago
Heavy rain threatens flood-weary Japan, Korean Peninsula
-
 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoEverything New On Netflix This Weekend: July 25, 2020
-
Finance3 months ago
Will Equal Weighted Index Funds Outperform Their Benchmark Indexes?
-
Marketing Strategies7 months ago
Top 20 Workers’ Compensation Law Blogs & Websites To Follow in 2020
-
 World News7 months ago
World News7 months agoThe West Blames the Wuhan Coronavirus on China’s Love of Eating Wild Animals. The Truth Is More Complex
-
Economy9 months ago
Newsletter: Jobs, Consumers and Wages
-
 Finance8 months ago
Finance8 months ago$95 Grocery Budget + Weekly Menu Plan for 8