Marketing Strategies
Small niche SEO Tips - Megathread
This article from Search Engine Journal inspired me to compile a way-too-long Twitter thread of SEO resources for small niches. I tried to recreate it here in it's entirety for you all.
If you feel like your niche is too small to reach effectively, don't give up! Narrow niche markets have unique SEO benefits. Once you crawl to the top of the SERPs, you essentially own the niche.
These 6 steps from @krisjonescom and @sejournal will help get you to the top.
STEP 1: Analyze Your Industry’s General Search Volume
1a) Google Keyword Planner is a good free tool for this, but it's not the only one. Ubersuggest by @neilpatel is another great free tool for discovering new keywords and keywords you already rank for:
1b) Snoop on your competition, too. See what they rank for and study what you can do to outrank them. The @semrush Keyword Gap tool is a great way to compare your domain against your competitors.
1c) Mine the SERPs. Here's how:
👉Manually look at the frontpage results for your keyword until you know the searcher's intent
👉Look at snippets
👉Click through the top 10 results and see what type of content they have
Take notes and include similar content in your articles.
STEP 2: Keyword Research
2a) Focus on keywords that match user intent. If you're selling a product, include keywords with transactional intent, but don't forget long-tail keywords. @answerthepublic is a unique tool for finding long-tail Q&A queries:
2b) Long-tail keywords are longer search phrases with fewer (but more than zero) monthly queries. They generally have lower search competition.
@Moz has a very thorough guide on keyword research and long-tail keywords:
2c) The keyword generator from @ahrefs is probably the best tool for identifying long-tail keywords around a central theme. Enter a word or two, then look for long-tail results.
2d) Using inanchor and intitle searches in @Google is an underused way to truly gauge keyword competition. It goes something like this:
🔸inanchor:"your keyword"
🔸intitle:"your keyword"
Fewer results = better chance of ranking.
The more monthly queries, the better.
STEP 3: Incorporate Keywords on Your Website
3a) Once you've settled on a keyword list, start creating optimized content on your site centered around these keywords. How do you optimize your content?
3b) Place your keywords in your
➡️Page Title
➡️Meta Description
➡️Body Content
➡️Header Tags
➡️URL
➡️Graphics (image alt and title text)
STEP 4: Create Great Content
4a) Remember when you mined the SERP results in Step 1c?☝️You did that for a reason. Model your content around existing successful pages, but do yours better. Be informative and write to your audience the way they were intending (match search intent)
4b) Put a strong focus on readability and properly format your content. Digital Marking becomes a lot easier once you build authority with an error-free site. @Grammarly will help ensure your content remains clear and error-free:
4c) Don't make walls of text. Incorporate visual elements and other mediums, like video, into your posts. If you don't have graphic design skills, use @canva. They have free graphic design tools and free courses to help develop your eye for visual design:
4d) Remember to apply the long-tail keyword tricks you learned in Step 3 to each of your articles. Your keyword optimized content is how you'll pass your competition in the SERPs.
Keyword-optimized content with good branding or your business is a bonus. Think infographics.
4e) Jump to the top of the SERPs with featured snippets. Google's featured snippets frequently come from pages outside the top 3 in the SERPs. Including lists and tables can help.
@michalpecanek and @ahrefs describe how to optimize for featured snippets:
STEP 5: Perform Technical SEO
5a) There are 3 main areas to focus on for technical SEO:
- Site Audit
- Mobile-Friendliness
- Website Security
5b) The SEO Spider Tool from @screamingfrog is one of the best tools for performing site audits. It gives you data on things like broken pages, mixed protocols and meta data issues on your site. Run it & fix any problems. Page speed is also important. 🐸
5c) Since Google crawls with mobile-first indexing in mind, you MUST make sure your site is mobile-friendly. @getbootstrap by @fat and @mdo is a responsive, beautiful and flexible theme perfect for SEO.
5d) Sites that are SSL secure receive an SEO boost from Google. Google has made it clear they favor secure https sites over unsecure sites. If you don't have an SSL certificate, install one at once. @letsencrypt has free SSL certificates:
🔐
STEP 6: Build Your Link Profile
6a) For this step, make sure your existing backlink profile is clean. Check your profile with backlink-checkers like @ahref or @Linkody. If your profile is spammy, disavow links with @googlewmc Search Console.
🔗
6b) @craigcampbell03 compares a bunch of these tools in the link below so take a look at it if you're not sure which one is best for you.
6c) Link building is hard, but you don't need to (and shouldn't) beg for backlinks. @brianclark from @copyblogger offers better strategies for natural link-building, including:
- Guest Posting
- Podcast Interviews
- Tribal Content
END OF THREAD
Thanks for reading all this! This compilation took me a really long time to make so if you enjoyed it, perhaps like or retweet the thread on Twitter:
None of these links go back to our site so I'm hoping it lands in your good graces 🙂
submitted by /u/wellsr
[comments]
Source link
Marketing Strategies
An SEO’s guide to event schema markup
. Tha30-second summary:
- From Google’s Cloud Next conference to Starbucks’ shareholder’s meetings, the live event industry has undergone a dramatic transformation in light of the global COVID-19 outbreak.
- As online services become more integrated into people’s lives, audiences expect more information that’s up-to-date and delivered quickly, including the events they plan on attending.
- This is where event schema markup can really help optimize event web pages so they show up on search results pages.
- Superb Digital’s Managing Director, Paul Morris shares a comprehensive guide on how to implement event schema markups that can win SERP rich results.
The live event industry has undergone a dramatic transformation in light of the global COVID-19 outbreak.
From Google’s Cloud Next conference to Starbucks’ shareholder’s meetings to live music performances, organizations and performers have had to move their in-person events online to curb the spread of the novel coronavirus while still addressing their audiences’ needs.
As online services become more integrated into people’s lives, audiences expect more information that’s up-to-date and delivered quickly, including the events they plan on attending. This is where event schema markup can really help.
What is an event schema markup?
Schema markup is code that helps search engines better understand what a web page is about in order to present more informative search results for users.
Instead of just basic HTML that points out what is the text or an image on a web page, schema markup provides context to information so that search engines know what content on a web page means.
Event schema markup is code that specifically points out to search engine facts relating to events, such as the location, schedule, organizer, and performers.
Schema markup is actually one of the multiple vocabularies that define terms and values in order to implement structured data (it just happens to be the most popular). In fact, Google, Yahoo, Bing, and Yandex have all collaborated to come up with Schema.org—an open community resource that provides schemas for their respective search engines to recognize.
What are the SEO benefits of using event schema markup?
Event schema markup can help your website’s search results ranking in a number of ways:
1. Rich results
Event schema markup provides specific facts that are immediately apparent on SERPs as rich results. Rich results are the details that appear in addition to the default blue links and text descriptions. They show important facts to users about a particular webpage and can include a multitude of things from reviews to recipes.
This has a two-pronged benefit. Rich results make for a better search experience for the users, first and foremost. Organizations, meanwhile, will stand out more in SERPs thanks to the eye-catching facts and visuals. On top of this, rich results also mean your webpage is occupying more screen real estate in the SERPs, pushing competitors further down the page.
2. Click-through rate (CTR) increase
One major effect of having rich results displayed for your webpages is that users are more likely to check out your site, instead of other sites that don’t show as much info. Your link will grab more attention.
Even if there will be users who are satisfied with just getting the bare minimum from the rich results, there is still a percentage that will click on your link to get more in-depth info or sign up as an attendee and book a spot.
3. Traffic boost
In line with getting higher CTR, your webpages that have event schema markup implemented can also enjoy higher traffic. Events platform Eventbrite is one of the strongest cases for event schema markup boosting traffic. They saw a 100% increase in the year-over-year growth of traffic from Google to their event listing pages.
Allen Jilo, an Eventbrite product manager, said that they saw a “visual difference in event search results on Google” within two to three weeks of event schema markup implementation.
4. Voice search optimization
Google Product Manager Aylin Altiok and Senior Engineering Manager for Google Search Will Lescszuk delivered a talk in Google I/0 2019 about the importance of structured data in improving the user search experience. In that talk, they mentioned that their motivation for schema markup was to be able to optimize content for both voice and search.
When you use event schema markup, you do not have to create two separate experiences to optimize for text and voice search. Apply it once and you can reach a bigger audience.
Google reported that voice made up 20% of searches in their app, and that was back in 2016. With digital voice assistants in use expected to reach eight billion by 2023, now is as good a time as any to start optimizing your event pages with schema markup.
What types of events can you markup?
Event schema markup can be used for a wide range of events, but there are still limitations that you need to respect if you don’t want to be penalized.
The event types that you can markup include:
- Business events
- Children events
- Comedy events
- Courses
- Dance events
- Deliveries
- Education events
- Exhibitions
- Festivals
- Food events
- Hackathons
- Literary events
- Music events
- Publication events
- Sale events
- Screenings
- Social events
- Sports events
- Theater events
- Visual arts events
You can also mark up a series of multiple events that have a connecting theme.
Do not markup business hours and promotions such as vacation packages, limited-time discounts, and coupons as events. Doing so runs the risk of your entire website being disqualified from showing rich results for any of your content.
How do I get my events to show up on Google?
First of all, you need to make sure your event pages can be crawled by Googlebot. If you use robots.txt or robots meta tags, they should allow Googlebot to index your event pages.
You should then implement schema markup in your event pages. Google only supports rich results for pages that feature a single event, so you should have individual pages for each of your events.
Required schema markup properties
There are three properties that an event page’s code needs for the page to show rich results on Google.
- location
- Name - Name of the venue
- Address - Detailed address
- name — Use the full title. Don’t include prices or promotions.
- startDate — The start date and time (if available) in the local timezone. If you don’t have an exact time, don’t specify it.
The following properties are not required, but they allow for more customization of rich results and a better overall user experience:
- description
- endDate
- eventAttendanceMode (critical for online-only events)
- image
- offers.availability
- offers.price
- organizer
- performer
Adding event schema markup
There are generally three ways to add event schema markup:
- Posting on third-party sites — The easiest way is to just post your events on big third-party events or ticketing sites like Eventbrite or Ticketmaster. These platforms are already integrated with Google, so they always show rich results for events related to particular search terms. Of course, these sites won’t be sending traffic to your website.
- Use platforms with built-in tools for schema markups — Ecommerce platforms like Magento and OpenCart already have structured data integrated. If you’re using a CMS such as WordPress, there are plenty of free plug-ins you can choose from to implement event schema markup easily.
- Coding — The third and hardest way is when you have a custom website that you can’t just use a plug-in with. This requires some coding but thankfully, you don’t have to be an expert web developer if you want to do it yourself.
How to add event schema markup yourself
The simplest method to add this code to your site is to use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper.
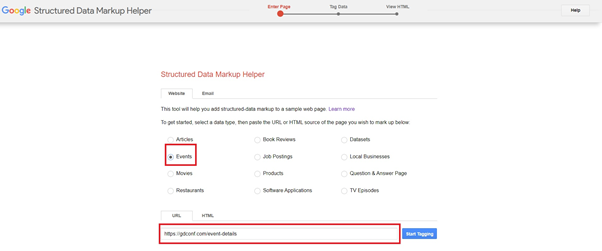
In the Enter Page section, select “Events” and type or paste the URL of the events page you want to markup on the bottom bar and click on Start Tagging.
In the Tag Data section, highlight the information you want tagged and choose the appropriate tag from the dropdown menu.
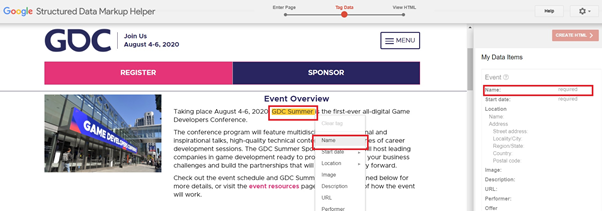
If there is info that isn’t present in the page that you believe should be tagged, click on the “Add missing tags” button on the bottom right. Supply the missing information in the following window.
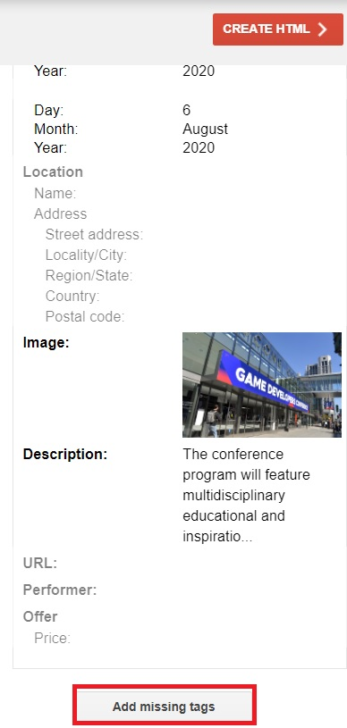
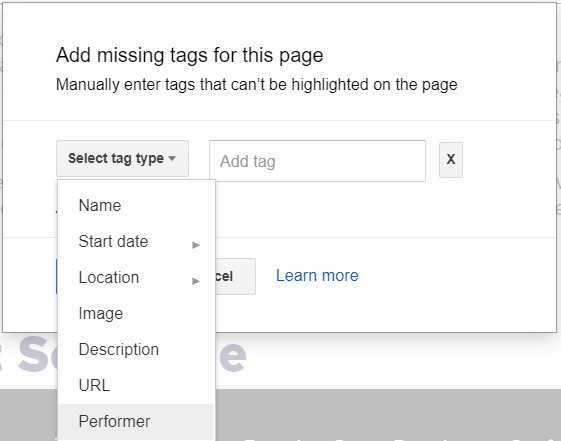
When you’re done adding all the important tags, click on the red “Create HTML” button on the top right. You should be taken to the View HTML section where you’ll see generated HTML code that has all the info you tagged.
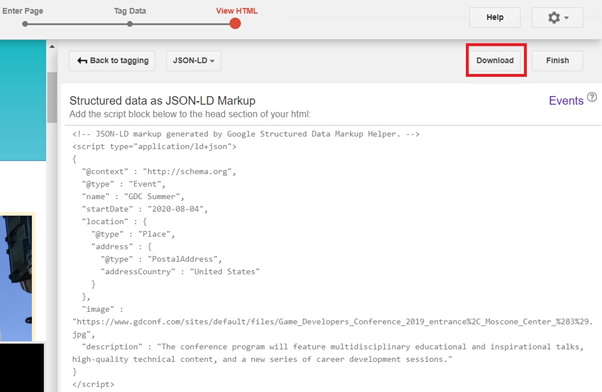
Click Download to download the HTML code, which you can then copy and paste below the <head> section of your event page’s HTML.
If you are hosting an online-only event, you will have to manually add a couple of lines of code since the Structured Data Markup Helper doesn’t have the option to indicate if the event is strictly virtual.
The code is as follows, with the sample URL in “url” replaced with the actual URL you’ll be using for your online event.
“eventAttendanceMode”: “https://schema.org/OnlineEventAttendanceMode”,
“location”: {
“@type”: “VirtualLocation”,
“url”: “https://sample.streamurl.com/”
},
How to test your event schema markup
Before you make wholesale changes to your site’s source code, you want to test the generated HTML to see if Google finds the corresponding page eligible for rich results. Fortunately, Google has just the tool for that—the aptly named Rich Results Test.
Click on the CODE tab, paste the HTML code generated by Structured Data Markup Helper onto the box, and click on the “Test Code” button.
If there are no errors in the code, the test results should show that the page is eligible for rich results.
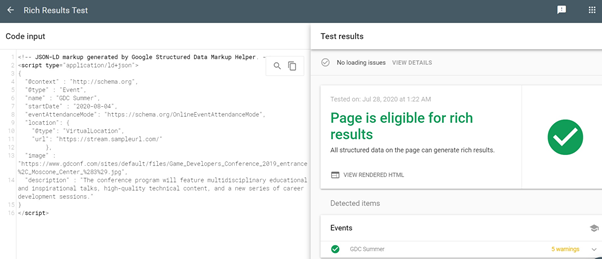
Note that the tool will show warnings despite its eligibility, if you don’t include all of the recommended tags for events, such as the name of the performer, the end date, and offers. If you have that information available, it’s highly recommended that you tag them in Structured Data Markup Helper.
Employ event schema markup for easy SEO wins
We may now be in a world where in-person events are a rarity, but that hasn’t curbed our desire for gatherings as we’re naturally social creatures. People will continue to want to take part in mass activities, whether that’s offline or online. Utilising event schema markup, your business can make the pivot towards more online events, whilst standing above the competition in the SERPs through rich results.
After reading this guide, you should find that it’s not actually too hard to make a start. “Start” is the keyword here, however, as more familiarity with coding can lead you to even deeper customization of your event pages’ HTML for better event search optimization. Schema.org has a whole page dedicated to all the properties you can use for events with examples in different formats that, with some studying, can take up plenty of valuable space on Google’s SERPs with the most detailed rich results.
Paul Morris is Managing Director of UK based SEO agency, Superb Digital.
The post An SEO’s guide to event schema markup appeared first on Search Engine Watch.
Marketing Strategies
What online shoppers want (and how you can provide it) [Infographic]
Being a working mom of two, I can honestly say that I would not be able to survive without online shopping.
Luckily for me, I’m doing this whole mom thing in 2019, when I can get groceries, diapers, clothes, dog food…I mean literally ANYTHING online!
With so many shopping choices out there, however, how can you as a marketer make sure you are giving them what they want and keep them coming back for more?
This infographic from, Yieldify, a customer journey optimization company, will tell you just that.
They surveyed over 1,000 online shoppers from the US and UK to find out what they want from their online shopping experience.
Curious if your want made the list? Let’s take a look and find out.
Do online shoppers want personalization?
Many would argue that our lives today are too public.
We share photos, stories, videos, and so much more over social media. We get very personal with people we may not even know.
So, it is no surprise that online consumers want a personalized shopping experience from brands we feel like we know.
In fact, 63% of all consumers expect that brands will have up to date information on their preferences across all channels.
The ironic part here is that 59% of these same consumers are not comfortable with websites tracking their behavior. In a post-GDPR world, 82% of consumers have become more aware of protecting their online privacy.
Interested in the latest on GDPR? Check out this article!
The beginning
All online purchases have a starting point.
What drove this particular consumer to make this particular purchase on this particular day?
The study shows that search is the clear leader here with 51% of all consumers saying their online purchase was driven by it.
Email also proved its worth with 17% of the audience saying a brand email drove them to make a purchase.
Referrals followed close behind with 9% of the consumers saying they made a purchase based on a friend’s recommendation.
So, you have site traffic, now what?
Once a consumer lands on your website, there are some simple things you can do to help guarantee a purchase:
-
Website usability: Make sure your website provides an easy and seamless experience.
-
Special offers: This can include something like free shipping or 10% off your first order.
-
Customer reviews: Users love to know that there are other satisfied customers so make sure they know that.
What if they don’t make a purchase? What are the most common reasons for cart abandonment?
-
Shipping charges are too high
-
The consumer wants to do more price comparison
-
Simply browsing but not ready to buy
-
A long checkout process
-
Negative reviews
Once a consumer converts you want them to come back and buy again.
You can help lock this in by gaining their trust, providing a great delivery and return policy, great website usability, positive reviews, and offering some kind of loyalty program.
There are so many features that you can and should include on an eCommerce website to make the usability experience a great one. Read more about that here.
Are you ready to give your online shoppers what they want? Read all the statistics for yourself in the infographic below and get started now.
Infographic by Yieldify
Marketing Strategies
What is an Email Funnel?
As a consumer—it would be nearly impossible to count the number of email funnels that have hit your inbox.
We can safely say, it’s been a lot. Businesses love email funnels because they swiftly move new subscribers toward their first purchase. Let’s take a look at the Customer Value Journey to get an idea of where your prospects are when they become subscribers.
The Customer Value Journey is the journey a prospect takes from finding out a business exists (Stage 1: Awareness) to becoming such a raving fan of it they’re actively promoting the business like a salesperson only they pay you (Stage 8: Promote).
When we talk about email funnels, we’re talking about the shift of a prospect choosing to become a subscriber (Stage 3: Subscribe) to buying your first offer (Stage 4: Convert).
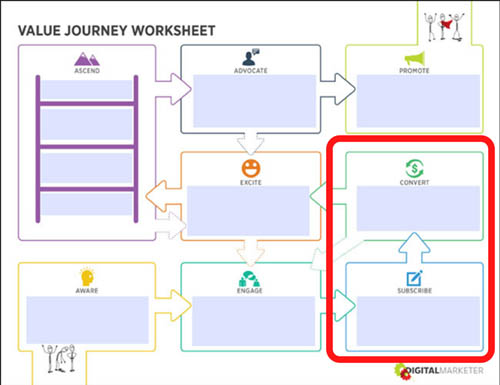
Email funnels are a big deal in the marketing world because they work… really, really well. People are still tuned into their inboxes, check out these statistics from OptinMonster:
- 99% of email users check their email every day
- 85% of the people you send an email to will receive your email
- More than 75% of teenagers still use email
Yep, you don’t need to figure out how to renegade on TikTok anytime soon; emails can reach every demographic you’re interested in.
How Email Funnels Work
Email funnels turn subscribers into customers by using specific strategies that sell products or services. We’ll get into those strategies in a minute, but first, take a look at the return businesses are seeing on their email funnels:
- For every $1 spent, email has an average ROI of $38
- Segmented campaigns can reach a 760% increase in revenue
- Compared to Facebook or Twitter, email is 40 times more effective at acquiring new customers
The number of emails you use in your funnel is going to depend on what you’re selling, but generally you’ll use a minimum of 4 and a maximum of 7. If your subscriber hasn’t converted by your seventh email about this offer—then you don’t want to keep bombarding them with it.
When you’re putting together your email funnel, you’re going to be highly focused on the copy you use. There are 4 emotional triggers to use in your email funnels:
- Gain: What does the subscriber gain by buying the product/service?
- Logic: Why does buying the product/service make total sense for them?
- Fear: What happens if they don’t buy the product/service?
- Scarcity: How long do they have to choose to buy this specific product/service?
Each email is going to follow a similar template:
- Introduction: Give a warm introduction to what you’re about to talk about (you wouldn’t walk up to somebody and start talking without at least saying a few introductory words first)
- Body: Use gain, logic, fear, and/or scarcity to show them why this offers matters to them NOW
- Close: Craft a clear call to action
- P.S. (Not always used): Add in extra gain, logic, fear, or scarcity
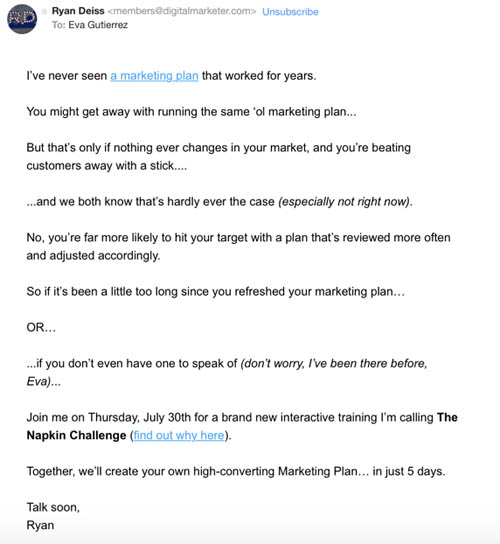
Here’s an example of an email funnel we ran for our Napkin Challenge. The first email uses logic and curiosity to drive the subscriber to want to create a marketing plan that gets them customers.
Subject Line: The napkin that cleaned up a $248k mess
Preview Text: A how-to guide for fixing a BIG problem

Touching on the fear business owners have over the complication of marketing these days, our second email was quick and to the point.
Subject Line: why is this so complicated?
Preview Text: Maybe marketing isn’t the problem.
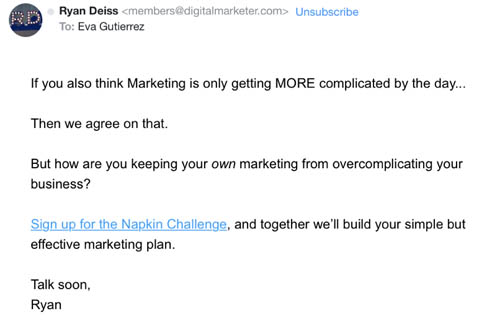
And then our third email used everything we know about the pain points of our avatars (thanks to the Customer Avatar Worksheet) to show them what they would gain from taking part in The Napkin Challenge.
Subject Line: time to hit the reset button
Preview Text: There’s no “do over” button, just “do better”
If you want to look at more email funnels, take a look at your inbox. Now that you’re familiar with what an email funnel is, you’ll realize that you’ve gotten a lot of these emails in the past. Some may have worked well (you bought the product) and others not so well (either the funnel was off, or you weren’t their target avatar).
Email funnels are a BIG part of marketing strategies because they’re the platform that moves subscribers from Stage 3 of the Customer Value Journey to Stage 4, the stage where they become first-time customers of your business.
And that’s a big deal for every business. 
The post What is an Email Funnel? appeared first on DigitalMarketer.
-
 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoBernice King, Ava DuVernay reflect on the legacy of John Lewis
-
World News3 weeks ago
Heavy rain threatens flood-weary Japan, Korean Peninsula
-
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoEverything New On Netflix This Weekend: July 25, 2020
-
Finance3 months ago
Will Equal Weighted Index Funds Outperform Their Benchmark Indexes?
-
Marketing Strategies7 months ago
Top 20 Workers’ Compensation Law Blogs & Websites To Follow in 2020
-
 World News7 months ago
World News7 months agoThe West Blames the Wuhan Coronavirus on China’s Love of Eating Wild Animals. The Truth Is More Complex
-
Economy10 months ago
Newsletter: Jobs, Consumers and Wages
-
 Finance8 months ago
Finance8 months ago$95 Grocery Budget + Weekly Menu Plan for 8